Essentials pre-commit git hook for Quality Software development
- Written by:
- Manav Kakani
- DevSecOps
- No Comments
In the fast-moving world of software development, it’s vital to make sure that high-quality code is added to repositories to keep software reliable and reduce technical problems. Pre-commit Git hooks are a very useful tool for making sure code meets standards, finding issues early, and promoting better development habits before changes are committed. This blog will explore the basics of pre-commit Git hooks, explain why they’re important, and show how to use them for quality software development.
What are git hooks?
Git hooks are scripts that automatically run at different stages of the Git process. These hooks let developers automate tasks such as running tests, checking for code style issues, or performing other checks before or after specific Git commands.
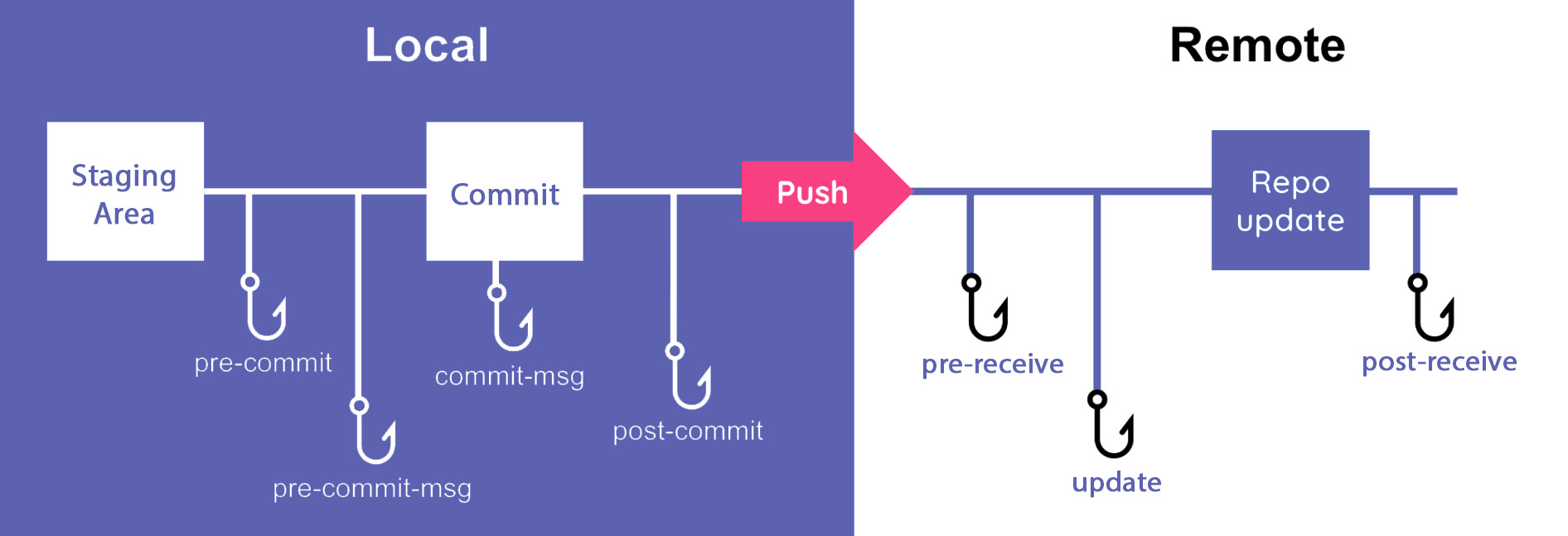
In this blog, we’ll focus on pre-commit hooks, which are part of the client-side hooks. These hooks run just before a commit is recorded, allowing developers to ensure that the code meets certain quality standards.
Why use pre-commit hooks?
- Catch errors early:
Pre-commit hooks help catch errors before they are committed to the repository. By setting up checks such as syntax validation, linting, and unit tests, developers can avoid introducing bad code.
- Maintain Code Quality:
Pre-commit hooks ensure that every commit meets a baseline level of quality. Automated checks like enforcing coding standards (e.g., PEP8 for Python) or detecting security vulnerabilities can help maintain a consistent codebase.
- Save Time and Resources:
Running automated tests and linters before committing saves time by preventing broken code from reaching the main branch. This reduces the need for reviewers to spot trivial mistakes and allows teams to focus on higher-level issues.
- Streamline Code Reviews:
When pre-commit hooks handle code formatting, linting, and other repetitive tasks, code reviewers can focus on the more important aspects—like the logic and architecture—rather than flagging minor issues like trailing commas or inconsistent indentation.
How pre-commit hooks work ?
Pre-commit hooks are stored in your repository’s .git/hooks directory and are executed automatically by Git before each commit. Each hook is essentially a script that Git runs before or after specific Git commands (like committing, pushing, or merging).
Here’s how it works in practice:
- After changes are staged (
git add). - Git runs the pre-commit hook script that defined in the
.git/hooks/folder. - If the script exits successfully (exit code 0), Git proceeds with the commit.
- If the script fails (non-zero exit code), the commit is blocked, and git notify to fix the issues.
Note: Pre-commit hooks can be written in any language executable by the system, such as Bash, Python, Node.js, or Ruby. As long as the script is executable, it can run checks before a commit. This provides flexibility to customize hooks based on the specific needs and environment of the project.
How to enable pre-commit hooks for use ?
Step 1 : Install Pre-commit
Pre-commit is a framework for managing and maintaining multi-language pre-commit hooks.
- Make sure you have Python installed.
- Install pre-commit using pip :
pip install pre-commit
Step 2 : Create or Modify .pre-commit-config.yaml
This file contains the configuration for your pre-commit hooks. You can add predefined hooks or create custom ones.
- In the root of your repository, create a file called “.pre-commit-config.yaml”.
- Add the hooks you want to use. For example:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0 # Use the latest version available
hooks:
- id: trailing-whitespace
- id: end-of-file-fixer
- id: check-yaml
- id: check-json
Step 3 : Install the Pre-commit Hooks
Once the .pre-commit-config.yaml is ready, you need to install the hooks for your repository.
- Run the following command to install the hooks:
pre-commit install
- This command sets up the pre-commit hooks in your
.git/hooksdirectory, so they automatically run before every commit.
10 cool pre-commit hooks for multi framework repository
Pre-commit hooks are a great way to automate checks before committing code to your repository. Writing pre-commit hooks in Bash is common because it’s lightweight and widely supported. Below are some practical examples that can be easily added to your Git project.
1. Linting Code
- ESLint/Prettier for JavaScript/TypeScript
- Use ESLint to automatically lint your JavaScript/TypeScript code and Prettier to format it.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-eslint
rev: v8.46.0
hooks:
- id: eslint
args: [--fix]
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-prettier
rev: V2.8.8
hooks:
- id: prettier
- Black for Python
- Automatically format your Python code using Black.
- repo: https://github.com/psf/black
rev: 23.1.0
hooks:
- id: black
- Rubocop for Ruby
- Lint and format Ruby code using Rubocop.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-rubocop
rev: v1.24.1
hooks:
- id: rubocop
2. Security Checks
- Bandit for Python
- Scan Python code for security vulnerabilities.
- repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit
rev: 1.7.4
hooks:
- id: bandit
3. Checking for Sensitive Data
- git-secrets
- Prevent committing passwords or secrets.
- repo: https://github.com/awslabs/git-secrets
rev: v1.3.0
hooks:
- id: git-secrets
name: "git-secrets"
entry: "git-secrets --scan"
language: system
- detect-secrets
- Scan for secrets in code to prevent them from being committed.
- repo: https://github.com/Yelp/detect-secrets
rev: v1.4.0
hooks:
- id: detect-secrets
args: ['--baseline', '.secrets.baseline']
4. Prevent Large Files
- Check for Large Files
- Prevent files over a certain size from being committed.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: check-added-large-files
args: ['--maxkb=500']
- git-lfs
- Automatically use Git LFS for large binary files.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: git-lfs
5. Enforce Commit Message Format
- Commitizen
- Enforce conventional commit messages.
- repo: https://github.com/commitizen-tools/commitizen
rev: v2.17.11
hooks:
- id: commitizen
- gitlint
- Check that commit messages follow specific style guidelines.
- repo: https://github.com/jorisroovers/gitlint
rev: v0.16.0
hooks:
- id: gitlint
6. Check for Merge Conflicts
- Conflict Marker Detection
- Detect merge conflict markers before a commit is allowed.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: detect-merge-conflict
7. Check for TODOs
- Check TODOs or Fixmes
- Prevent commits containing TODO or FIXME comments.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: forbid-todo
8. Trailing Whitespace and End-of-File Check
- Remove Trailing Whitespace
- Remove trailing whitespace automatically.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: trailing-whitespace
- Ensure End-of-File Newline
- Ensure a newline is added at the end of files.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: end-of-file-fixer
9. YAML/JSON Validation
- YAML Linting
- Validate and lint YAML files.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: check-yaml
- JSON Linting
- Validate JSON files.
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v4.3.0
hooks:
- id: check-json
10. Dockerfile Linting
- Hadolint
- Lint your Dockerfile for best practices.
- repo: https://github.com/hadolint/hadolint
rev: v2.12.0
hooks:
- id: hadolint
Conclusion
Pre-commit Git hooks act as a quality control system, running in the background to ensure that code meets required standards. They help catch errors early, enforce consistent coding styles, and prevent accidental commits of broken code or sensitive data. Incorporating pre-commit hooks into the workflow ensures that the codebase remains clean, secure, and consistent from the first commit. Implementing them can lead to a more efficient and error-free software development process.