- Written by:-
- Nensi Sukhadiya
- AWS
- No Comments
Managing Amazon RDS efficiently becomes challenging as applications evolve. Over time, databases often end up with over-allocated storage, outdated engine versions, or instance types that no longer match actual workloads. Unfortunately, Amazon RDS does not allow you to directly reduce allocated storage on an existing database instance.
Traditional approaches to fix this usually involve creating a new database, migrating data manually, updating application endpoints, and accepting downtime all of which introduce risk and operational complexity.
This is where AWS RDS Blue/Green Deployment provides a clean and reliable solution. It allows you to create a parallel database environment, apply storage and configuration changes safely, and switch production traffic with minimal downtime and no application changes.
What Is AWS RDS Blue/Green Deployment?
AWS RDS Blue/Green Deployment is a deployment model that allows database changes to be prepared in a parallel environment while the production database continues to run uninterrupted. In this model, AWS maintains two database environments at the same time: Blue and Green.
The Blue environment represents the current production RDS database that actively serves application traffic. Alongside it, AWS creates a Green environment, which is a fully managed staging database. The Green database is initially created as an exact copy of the Blue database and stays continuously synchronized through replication, ensuring data consistency between the two environments.
All database-level and infrastructure-level changes are made only in the Green environment. This includes adjustments to database configuration, engine versions, instance class, and storage settings. Because the Green environment is isolated from live traffic, these changes can be applied, tested, and validated without affecting the running application.
Once the Green environment is ready, AWS performs a controlled switchover. During this process, the Green database is promoted to production and begins handling application traffic, while the original Blue database is retired. The database endpoint remains the same, so applications do not require configuration changes.
This parallel deployment approach enables database changes to be executed in a controlled and predictable manner, setting the foundation for safely modifying storage and infrastructure characteristics without direct impact on the production system.
Why Use AWS RDS Blue/Green Deployment for Reducing RDS Storage
Reducing RDS storage is fundamentally different from increasing it. Since AWS does not allow shrinking storage on an existing instance, the only safe way to do so is by creating a new database with the desired storage size. Blue/Green deployment automates this process while eliminating the risks associated with manual migrations.
With Blue/Green deployment, the existing database continues serving production traffic while AWS creates a fully managed Green database with the new storage configuration. Because both environments are kept in sync through continuous replication, data consistency is maintained throughout the process. This approach significantly reduces downtime, avoids manual intervention, and removes the need for application-level changes.
Another major advantage is the ability to combine storage reduction with other improvements. While setting up the Green environment, you can upgrade the database engine, switch to a more cost-effective instance class, and move from gp2 to gp3 storage. Instead of handling these changes separately, Blue/Green deployment allows them to be applied together in a controlled and production-safe manner.
How It Works
Blue/Green deployment works by running two database environments in parallel.
Blue Environment (Production): This is the existing RDS database that handles live application traffic. It continues operating normally throughout the process.
Green Environment (Staging): AWS creates a new database the Green environment that starts as a copy of the Blue database, stays continuously synchronized through replication, and can be modified independently. All planned changes, such as reducing storage, upgrading the database engine, changing the instance type, and modifying the storage volume, are applied only in the Green environment.
Switchover: Once validation is complete, AWS performs a switchover. During this process, writes are briefly paused, a final replication sync is completed, and the Green database is promoted to production. The database endpoint remains unchanged. Downtime is minimal and typically unnoticeable to users.
Prerequisites
Before starting a Blue/Green deployment for reducing RDS storage, it is important to ensure that the existing RDS instance is healthy and stable. Automated backups should be enabled, and taking a manual snapshot beforehand is strongly recommended as a safety measure.
You should also verify that your RDS engine and region support Blue/Green deployments. Proper IAM permissions are required to create and manage RDS instances and perform the switchover. Additionally, it is important to decide on the target configuration in advance, including the reduced storage size, desired engine version, instance class, and storage type.
From an application perspective, the workload should be able to tolerate a brief connection interruption during the switchover. This is typically handled through retry logic or connection pooling, which are already considered best practices for production systems.
Steps to Perform
Here is an overview of how the AWS Glue ETL pipeline works.
1. Prepare the Existing RDS Instance
Ensure you have an existing Amazon RDS instance in a healthy state. In this example, an AWS MySQL RDS instance with 30 GB of allocated storage is used as the Blue (production) database.

2. Start Blue/Green Deployment Creation
Open the Amazon RDS console, select the RDS instance, and navigate to Actions → Create Blue/Green deployment.
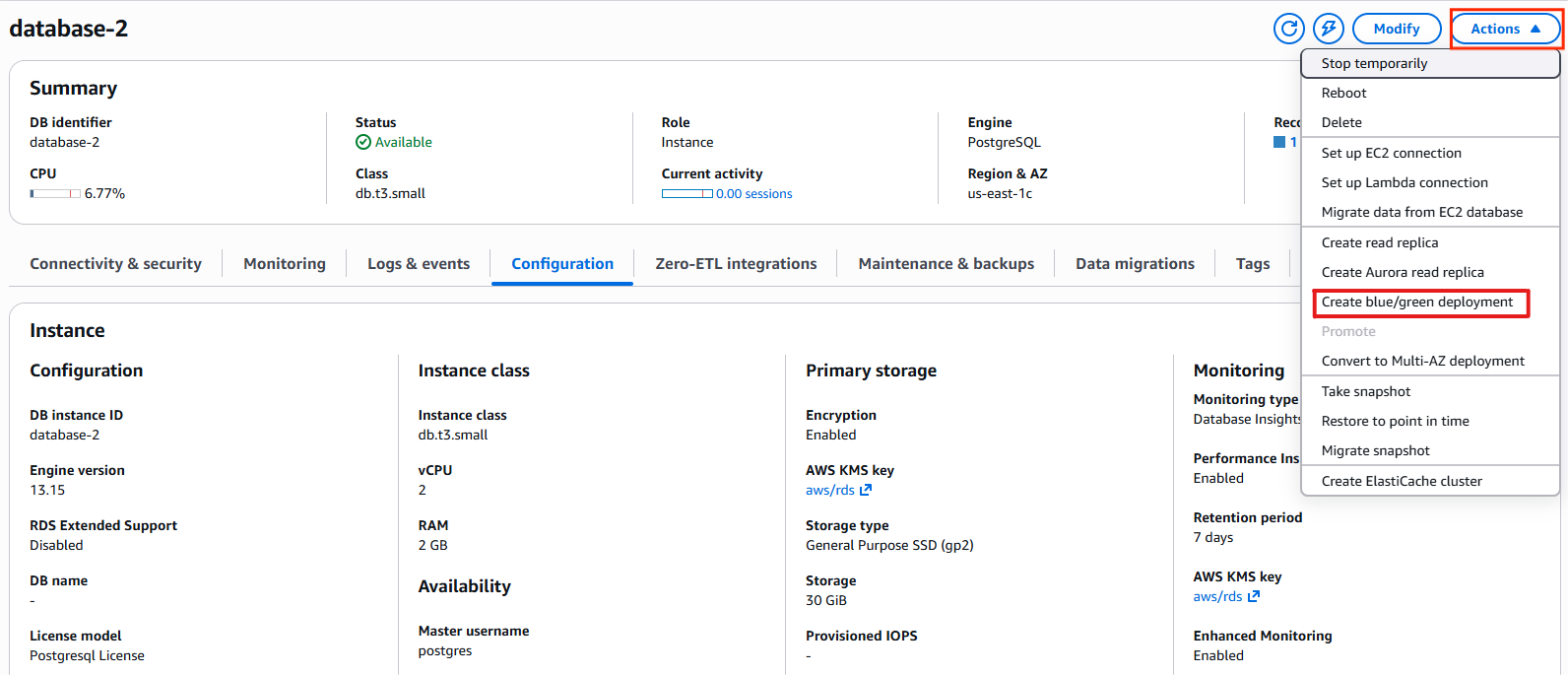
3. Validate Prerequisites
Before creating the deployment, confirm that automated backups are enabled on the RDS instance. Also ensure that the RDS master password is managed manually. If AWS Secrets Manager is enabled, switch to manual password management.
4. Configure the Green Environment
While creating the Blue/Green deployment, provide a meaningful deployment name. Select the target MySQL version, choose updated DB parameter groups if required, pick the desired DB instance class for the Green environment, and specify the reduced storage size.
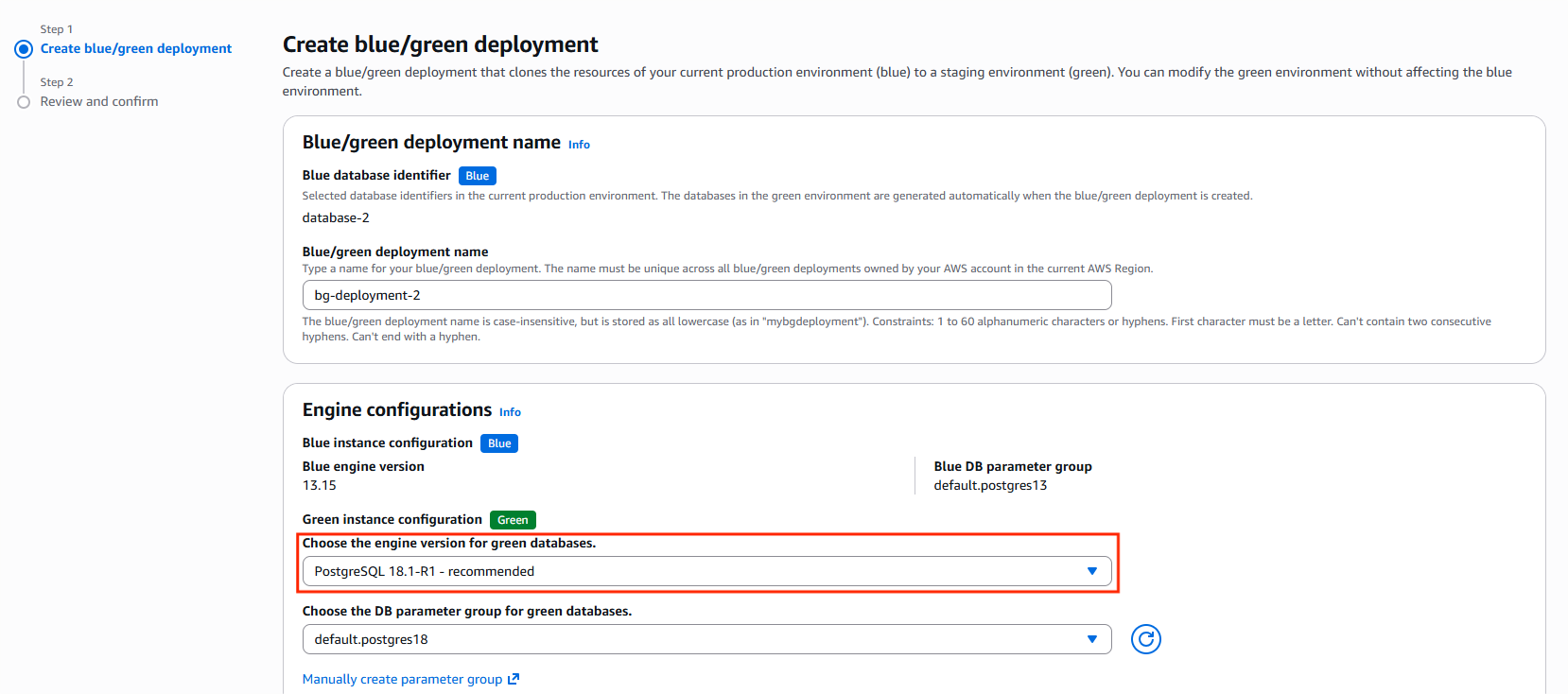

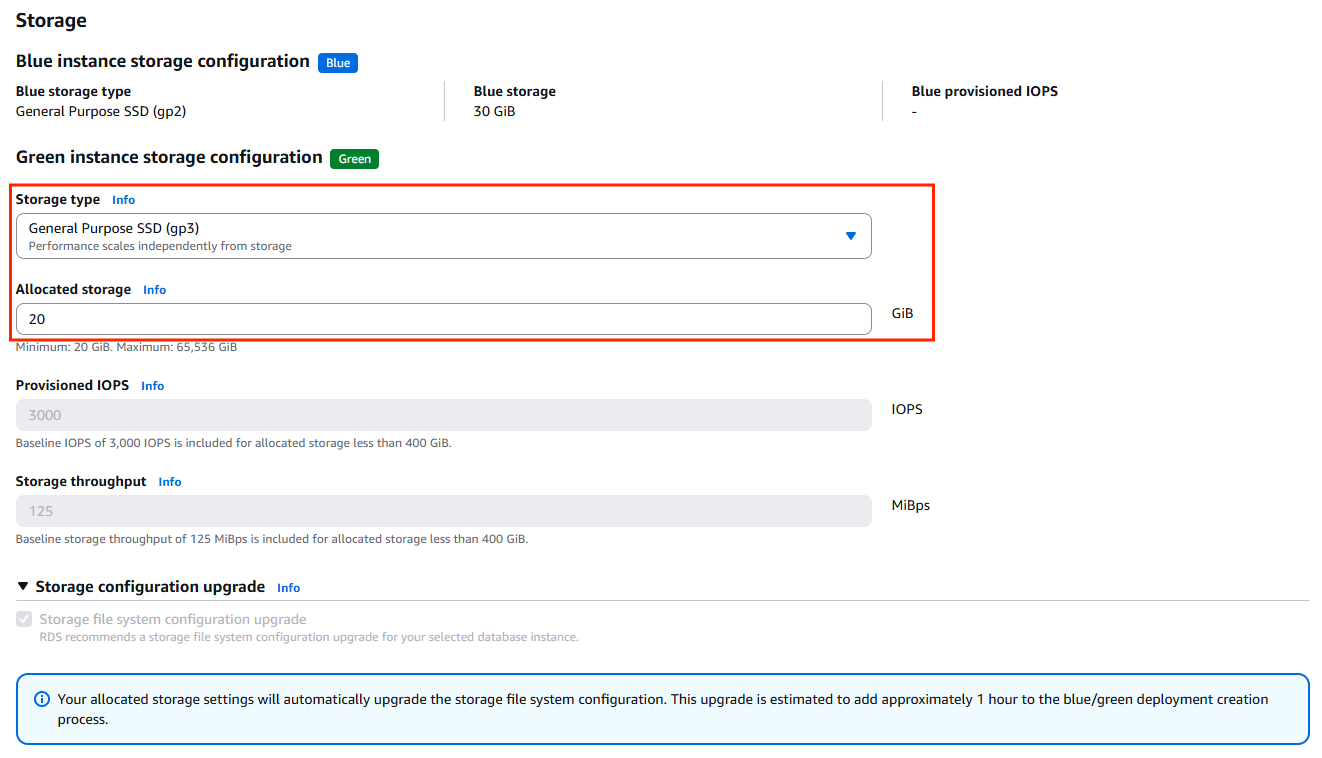
5. Review Configuration Differences
Review the differences between the Blue and Green instances. In this example, the MySQL engine is upgraded to version 8.4.4, and the allocated storage is reduced from 30 GB to 20 GB. All configuration changes applied to the Green instance are clearly displayed.
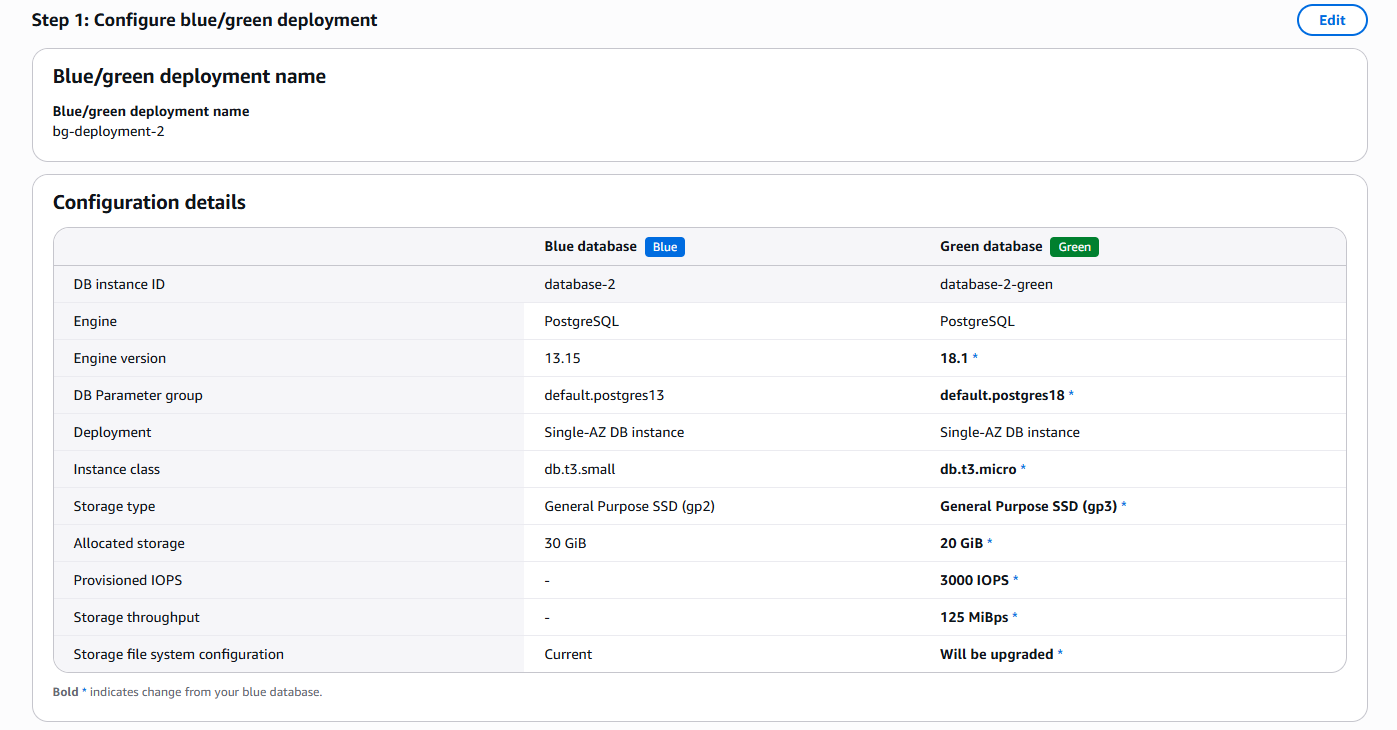
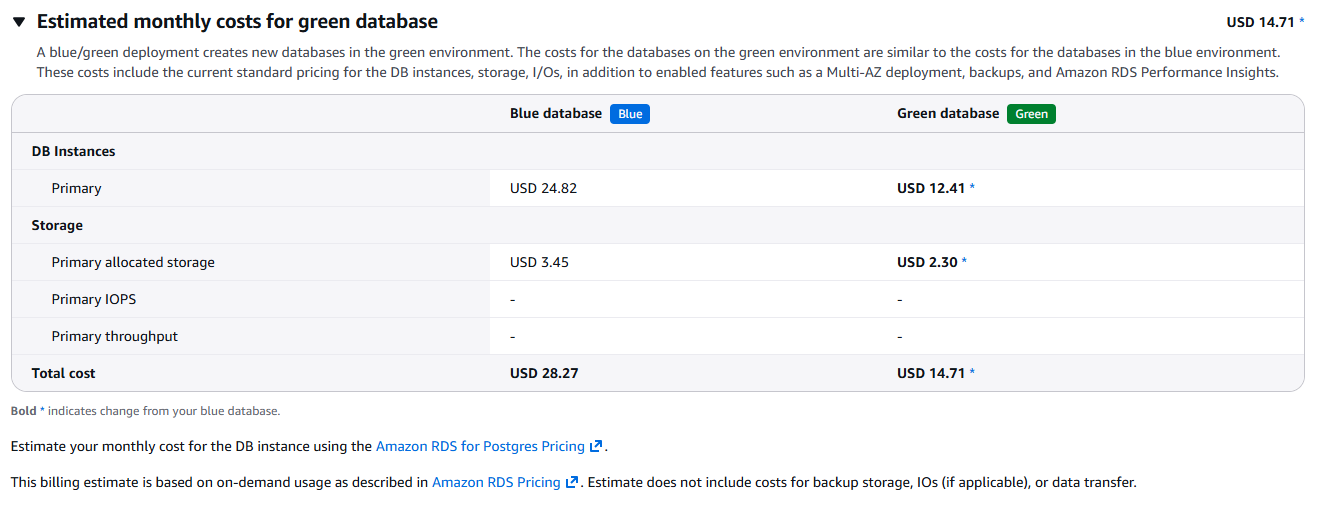
6. Review Cost Impact and Create Deployment
Check the estimated pricing changes to understand the cost impact, then proceed to create the Blue/Green deployment.
7. Wait for Deployment Readiness
Wait until the Blue instance, Green instance, and the Blue/Green deployment are all in the Available state.
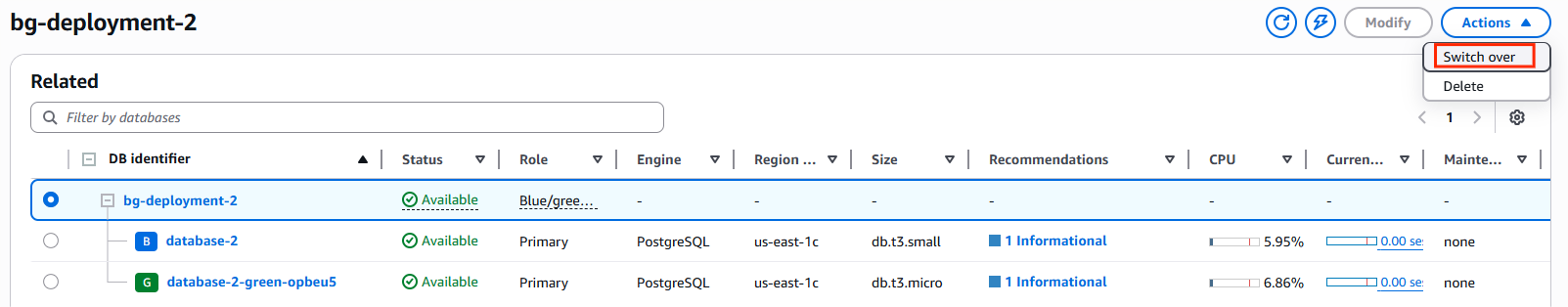
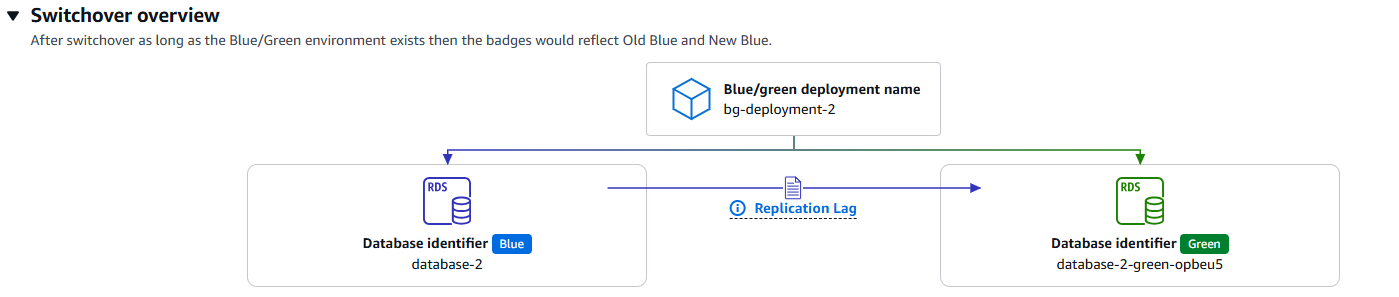
8. Perform the Switchover
Initiate the switchover by navigating to Actions → Switch over. Configure the timeout settings based on your application’s tolerance for brief connection interruptions.
9. Verify Production Traffic
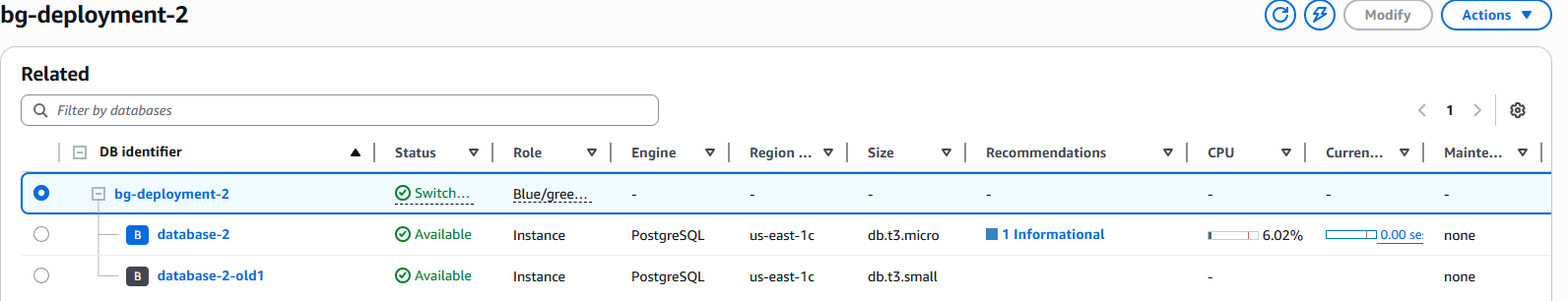
After the switchover completes, the original RDS endpoint is reassigned to the Green instance, which now serves as the new production database. Verify application functionality and database connectivity.
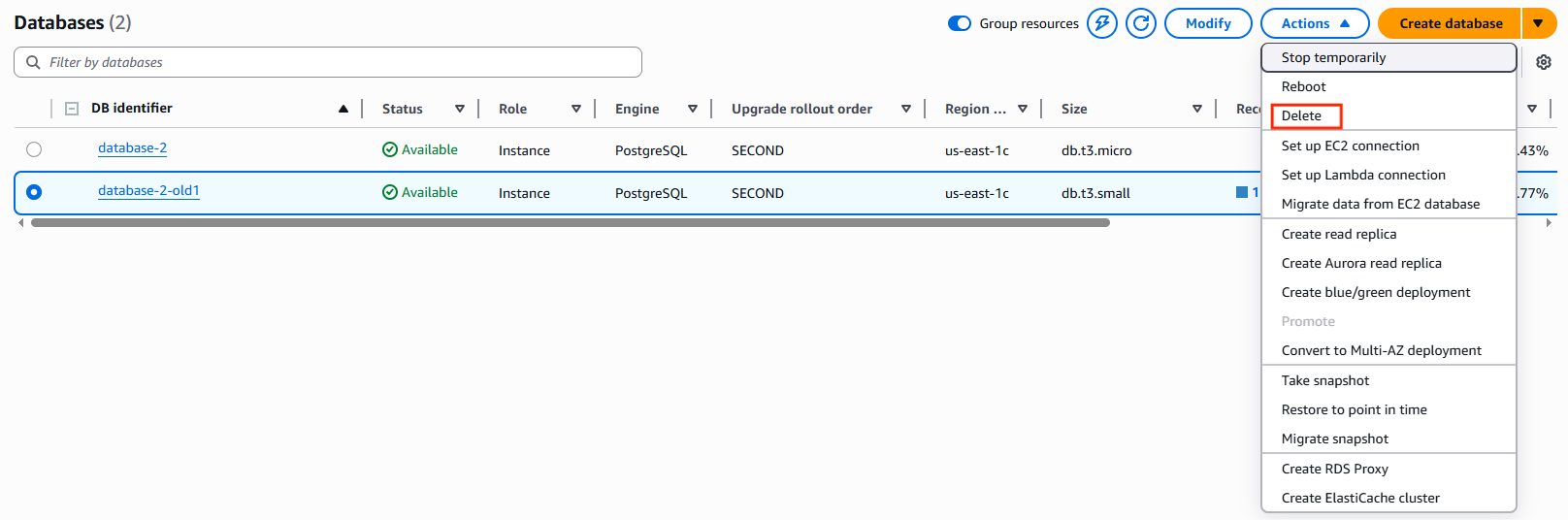
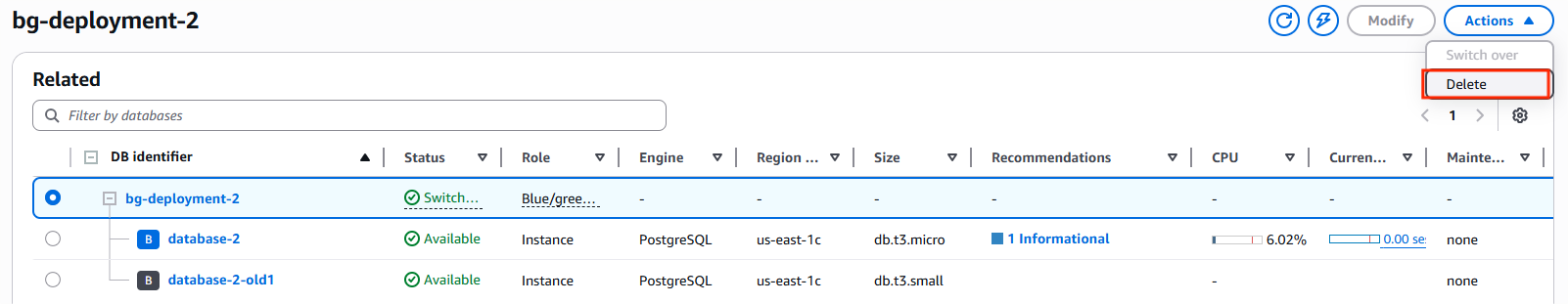
10. Clean Up Old Resources
Once validation is complete, delete the Blue/Green deployment and remove the old RDS instance if it is no longer required to avoid unnecessary costs.
Final Thoughts
Reducing Amazon RDS storage has traditionally been a difficult task, often involving complex migrations and noticeable downtime. AWS RDS Blue/Green Deployment simplifies this process by offering a fully managed and production-safe way to right-size storage while also handling engine upgrades, instance changes, and overall cost optimization.
By running two environments in parallel, keeping them continuously in sync, and performing a controlled switchover, Blue/Green deployment removes much of the risk usually associated with database changes. There is no need for manual data migration or application reconfiguration, which makes the entire process far more predictable and less stressful for operations teams.
If your RDS database is over-provisioned or approaching an upgrade cycle, AWS RDS Blue/Green Deployment provides a reliable and practical approach to optimizing storage and modernizing your database infrastructure without disrupting your application or users.