Implementing AWS Recycle Bin with locked tag level plus Region level retention rules strengthens DevOps operations against accidental plus malicious deletions. By tailoring retention periods to match application workflows integrating rule creation through infrastructure as code plus monitoring usage continuously teams gain reliable protection without extra feature costs. Enabling AWS Recycle Bin today helps keep AWS infrastructure resilient recoverable plus prepared for unexpected failures.
- Written by:-
- Siddhant Gayakwad
- AWS
- No Comments
Accidental deletions in AWS are more common than expected. A snapshot removed during cleanup an AMI deleted by mistake or an automation script running with incorrect settings can quickly become a serious problem. AWS Recycle Bin works as a safety layer that helps DevOps teams recover deleted EBS snapshots and AMIs before they are permanently lost. Additionally by retaining deleted resources for a defined period teams gain enough time to restore critical data and reduce downtime. Furthermore for DevOps engineers working with EC2 EKS and automated CI CD pipelines AWS Recycle Bin transforms risky errors into controlled and manageable recovery actions.
What is AWS Recycle Bin?
AWS Recycle Bin is a built in data recovery feature that helps protect critical AWS resources from accidental deletion. When resources such as EBS snapshots or EBS backed AMIs are deleted they are not removed right away. Instead AWS temporarily stores them in the Recycle Bin based on a retention rule defined by the user.
Each retention rule defines how long a deleted resource remains recoverable. For example EBS volumes can be retained for up to 7 days while snapshots and AMIs can be stored for up to 365 days. During this time DevOps teams can restore the resource easily with all metadata preserved.
This feature is especially valuable in environments that rely on automation CI CD pipelines and frequent cleanup activities. A small mistake misconfiguration or script failure can otherwise cause permanent data loss. AWS Recycle Bin acts as a safety buffer that helps teams recover quickly and continue operations without stress.
Why DevOps Teams Need It?
DevOps teams operate in fast paced environments where speed automation and frequent deployments are part of daily work. Infrastructure is commonly managed through scripts CI CD pipelines and automated cleanup jobs. While this approach improves efficiency it also increases the risk of accidental deletions caused by misconfigured scripts incorrect filters or simple human mistakes.
AWS Recycle Bin adds a strong safety layer by making sure important resources are not permanently deleted right away. Instead it offers a recovery window where deleted snapshots or AMIs can be restored without rebuilding systems from the beginning. This becomes especially important during high pressure incidents when fast decisions may lead to costly errors.
For teams managing EC2 fleets Kubernetes clusters on EKS or backup driven rollback strategies snapshots play a critical role. Losing them can affect recovery time objectives and may even cause downtime. By using AWS Recycle Bin DevOps teams lower recovery risks improve operational stability and gain confidence to move quickly without the fear of irreversible data loss.
Core Safeguards to Implement
To get the most value from AWS Recycle Bin DevOps teams should define clear intentional retention rules. These rules determine which resources are protected and how long they can be recovered after deletion. Without proper safeguards critical data may still be lost or retained longer than required.
Start by using tag based retention rules. Tags such as Environment Production or Backup Critical help identify resources that need higher protection. When these tags are applied AWS Recycle Bin protects only important snapshots and AMIs while leaving non critical resources unaffected.
For wider coverage Region level rules can be applied to protect all supported resources within a specific AWS Region. This approach helps prevent accidental deletions across large environments. Exclusion tags can also be used to avoid retaining temporary or test resources.
Another key safeguard is rule locking. By locking retention rules with an unlock delay of 7 to 30 days teams can prevent accidental or malicious changes even from administrators. This adds an extra layer of security and keeps recovery policies enforced during critical situations.
The Recycle Bin supports the following resource types.
- Amazon EBS snapshots
- Amazon EBS backed Amazon Machine Images
- Amazon EBS volumes.
Initiating Recycle Bin
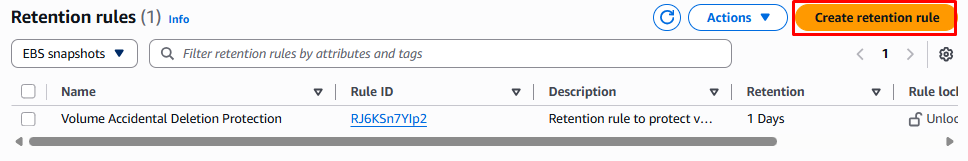
Our goal is to recover an EBS snapshot if it gets deleted. Select the snapshot and click the Recycle Bin option. This action redirects you to the Recycle Bin page where you can click Create retention rule to proceed.

Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Step 1: Create a Retention Rule
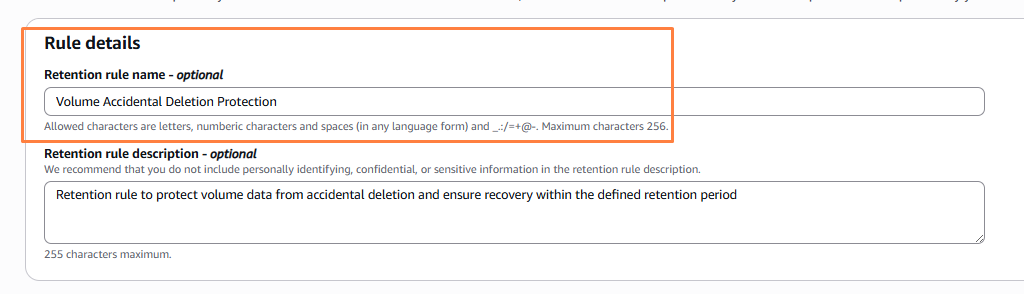
To start with, we require the retention rule name and descriptions.
Step 2: Choose Resource Type
Retention settings allow us to decide which resources we want to protect such as AMIs or EBS snapshots. We can select resources using specific tags or apply protection to a defined group of resources. These settings also let us choose how long deleted resources should be retained which defines the recovery time available after deletion.
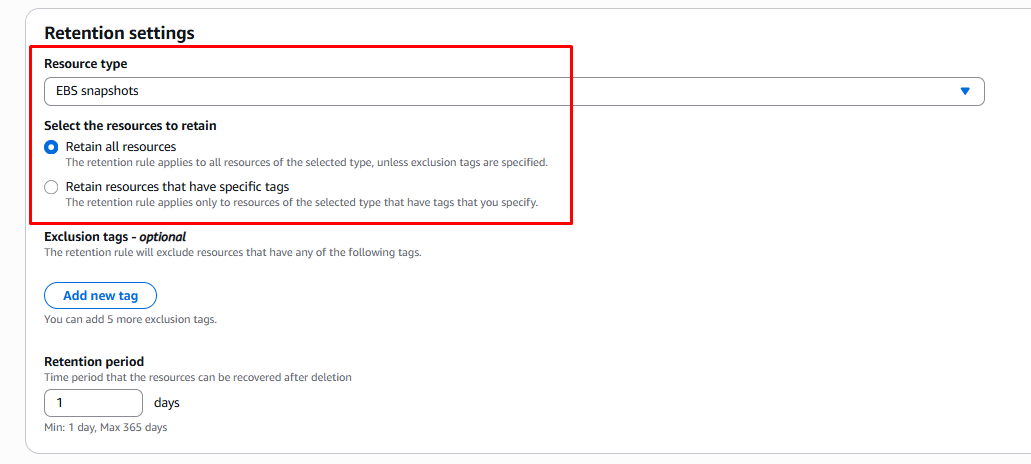
In this example we selected Apply to all resources to keep the setup simple and avoid extra configuration.
Recovering Deleted Snapshot
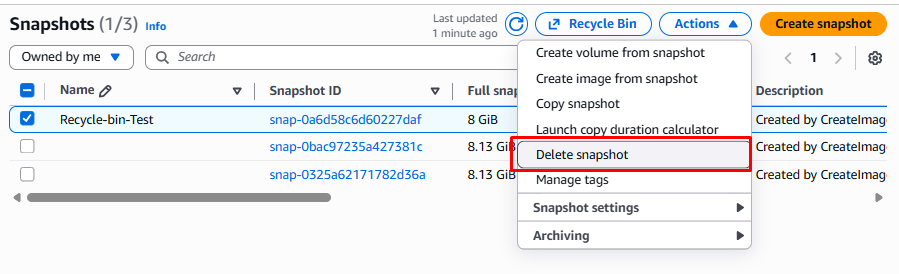
Below we delete the snapshot so it no longer appears in the Snapshots list. Later we realize a mistake was made so we go to the Recycle Bin to recover it.
Step 3: Delete the Resource for Testing
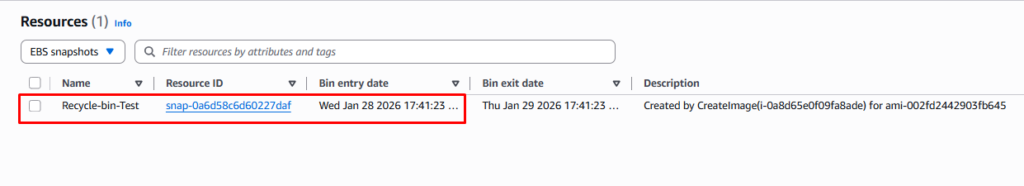
Step 4: Verify Resource in Recycle Bin
Under Resources in Recycle Bin we can recover the deleted EBS volume as shown below.
Step 5: Recover the Resource
To recover the snapshot, select the snapshot name from the list and click the Recover button.
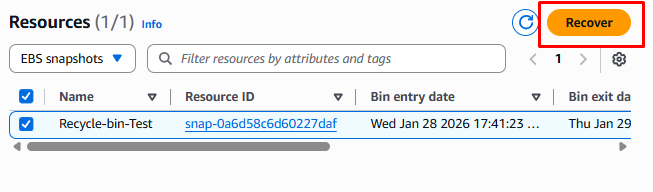
Step 6: Validate Recovery
After clicking the Recover button the snapshot is restored and appears again in the Snapshots list ready for use.
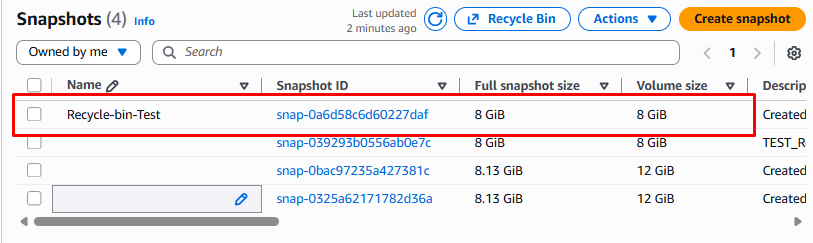
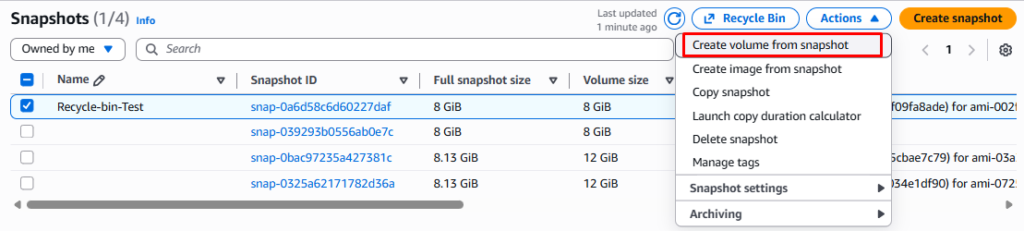
From this snapshot we can create a new EBS volume. We can also create an AMI image in any Availability Zone as shown below.
Recycle Bin For AMI
Click on Create retention rule to define how AMIs should be protected after deletion
Step 1: Create a Retention Rule
To begin we need the retention rule name plus a short description.

Step 2: Set Retention Period
Define Retention Period
Set how long deleted AMIs should stay in the Recycle Bin before permanent deletion.
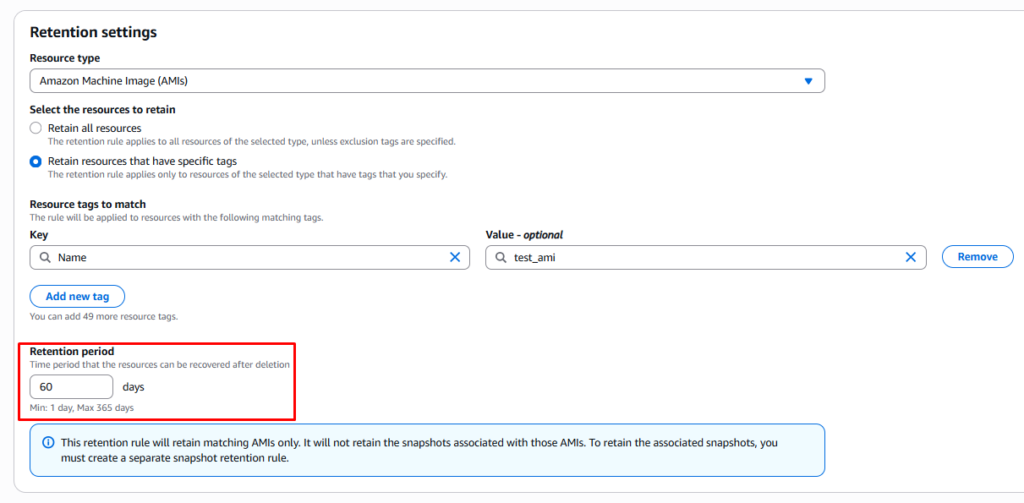
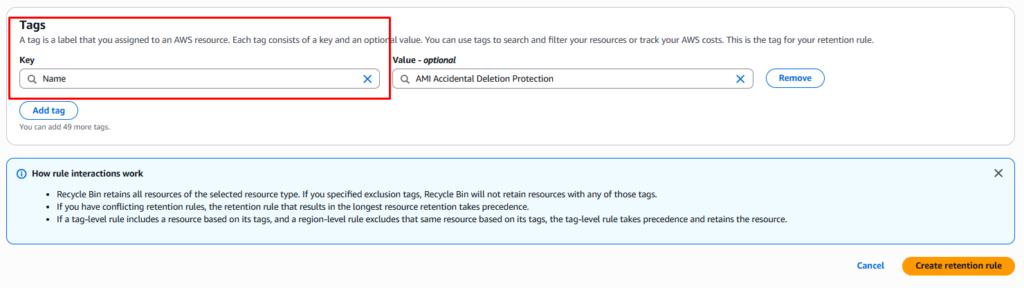
Step 3: Review Scope, Apply Tags, and Create Rule
Choose whether the rule applies to specific AMIs using tags or covers the entire Region. Review the configuration then create the rule to enable AMI protection.
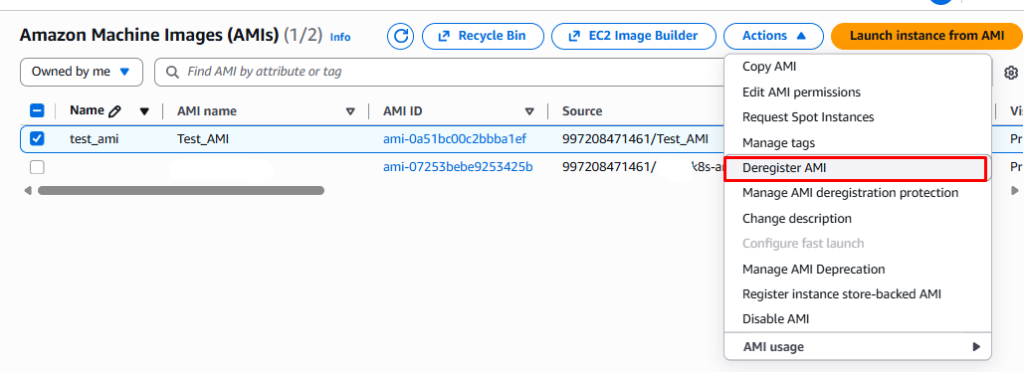
Step 4: Recovering Deregister AMIs
Below we deregister the AMI so it no longer appears in the AMI list. Later we realize a mistake was made so we navigate to the Recycle Bin to recover it.
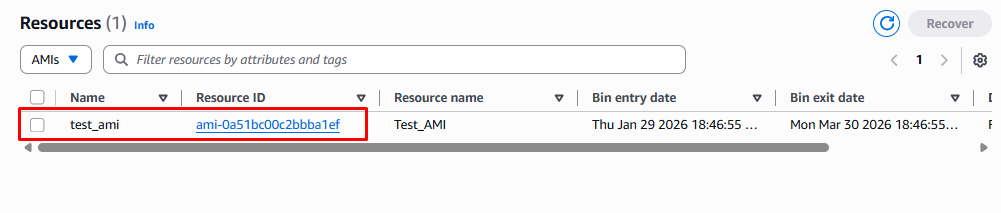
Under Resources in Recycle Bin we can recover the deregistered AMI as shown below.
Step 5: Delete the Resource for Testing
To recover the AMI select the AMI name from the list then click the Recover button.
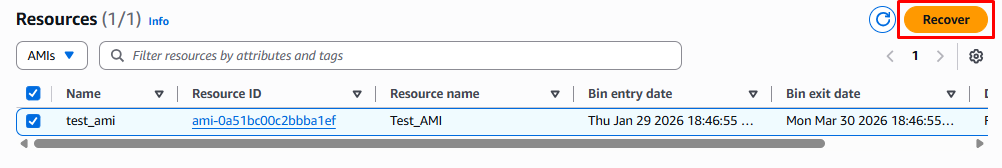
Note :Before restoring an Amazon Machine Image from AWS Recycle Bin make sure all related EBS snapshots are restored first. An AMI depends on its snapshots so recovery will fail if they are still deleted or present in Recycle Bin. Always restore the required snapshots before recovering the AMI.
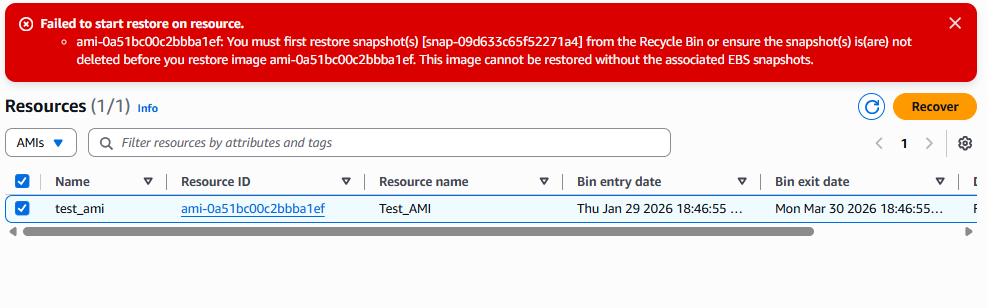
Step 6: Recover the Resource
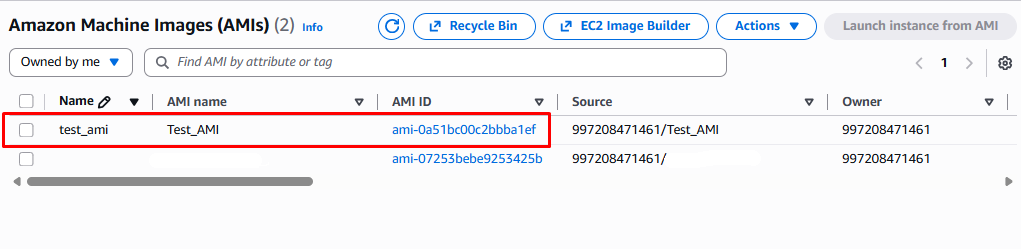
After clicking the Recover button the AMI is restored and appears again in the AMI list ready for use.
Navigate to AWS Recycle Bin from the AWS Management Console then confirm the correct Region is selected. Create a retention rule and choose the resource type such as EBS snapshots. Decide whether the rule applies at the Region level or only to resources with specific tags. Set the retention period such as 14 days which defines how long deleted snapshots remain recoverable. For added security lock the rule during creation with an unlock delay such as 7 days to prevent accidental or unauthorized changes.
For teams that prefer automation the same setup can be created using the AWS CLI. The command below creates a retention rule that protects EBS snapshots tagged with Environment=Production for 14 days.
.bash
aws rbin create-rule \
--resource-type EBS_SNAPSHOT \
--rule-name "ProdSnapshots" \
--tag-filters Key=Environment,Value=Production \
--retention-period 14After the rule is created you can test it by deleting a snapshot that matches the tag filter. The deleted snapshot will appear in Recycle Bin where it can be restored during the retention period.
There are Three types of retention rules with Recycle Bin
| Safeguard Type | Description | Retention Options | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tag-Level Rules | Apply to resources matching key:value tags (up to 50 pairs per rule) | 1-365 days (snapshots/AMIs), 1-7 days (volumes) | Selective protection for prod resources |
| Region-Level Rules | Protect all in Region, exclude by tags | Same as above | Broad coverage with exceptions |
| Rule Locking | Prevents edits/deletes requires unlock delay | N/A | High-security environments |
Advanced Configurations and Best Practices
• Infrastructure as Code Integration
Define AWS Recycle Bin retention rules using AWS CloudFormation to support consistent repeatable deployments across multiple accounts Regions. This approach reduces manual errors plus configuration drift.
• Controlled Access with IAM
Restrict Recycle Bin restore permissions to designated recovery administrators using IAM policies. This ensures only approved users can perform recovery actions while maintaining operational security.
• Organized Rule Management
Tag Recycle Bin rules to improve visibility plus organization across environments. Avoid adding sensitive information in rule names or descriptions to keep configurations secure.
• Audit Visibility
Enable AWS CloudTrail logging for all Recycle Bin actions including deletions plus restores. This provides a clear audit trail to support compliance plus incident investigations.
• Event Driven Notifications
Use Amazon EventBridge to trigger alerts when resources enter Recycle Bin. This helps teams detect unexpected deletions early plus respond quickly.
• Quota Awareness
AWS allows up to 250 Recycle Bin rules per Region. Monitor usage through AWS Service Quotas to avoid hitting limits as environments scale.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Recycle Bin rules can be automated through Terraform modules or Jenkins pipelines using the AWS provider to ensure consistent protection across environments. Apply production tags before deployment so retention rules automatically protect EBS snapshots created by EKS persistent volumes or SageMaker workloads. For Kubernetes environments Helm charts can tag PVC backed snapshots automatically which improves cluster level disaster recovery without manual effort.
Monitoring and Cost Optimization
Recycle Bin usage can be monitored using CloudWatch metrics along with the aws:recycle-bin:resource-in-bin cost allocation tag to track storage costs. Resources stored in Recycle Bin continue to incur standard EBS charges until the retention period expires while the Recycle Bin feature itself has no additional cost. To optimize spending teams should set shorter retention periods for development environments plus use CloudTrail alerts to detect unusually high deletion activity.
Real-World Use Cases
In day to day operations DevOps teams often rely on EBS snapshots during cluster upgrades or major infrastructure changes. If a snapshot is deleted by mistake during these activities AWS Recycle Bin allows teams to restore it within minutes which reduces downtime plus avoids complex recovery steps.
During security incidents such as ransomware attacks or compromised credentials locked Recycle Bin rules play a critical role. Even if an attacker attempts to delete backups rule locks prevent immediate removal which gives teams valuable time to investigate contain the issue plus recover data safely.
AWS Recycle Bin also protects against unintended effects of cost optimization scripts. Automated jobs that clean up old or unused snapshots can sometimes remove critical backups. By using tag based retention rules DevOps teams keep important snapshots protected while still allowing safe cleanup of non critical resources.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
• Missing Region Coverage
Recycle Bin rules are Region specific. Create rules in every active Region to prevent unprotected resources in multi Region environments.
• Overly Broad Retention Rules
Wide scoped rules can increase storage costs by retaining unnecessary snapshots. Use tag based rules plus exclusions to protect only critical resources.
• Unlocked Production Rules
Unlocked rules can be changed or deleted by mistake. Lock production retention rules with an unlock delay to maintain continuous protection.
